What are Functional Groups?
Halides:
- Functional Group:
- -F, -Cl, -Br, -I
- General Formula:
- R-X
- Naming:
- Name the parent chain (methane, ethane, propane...)
- Name halogen groups as side chains (fluoro-, chloro-, bromo-, iodo-)
- Name other side chains
- Examples:
- CH3Br --> bromomethane
- CCl4 --> tetrachloromethane
- H2FCCHFCH2CH3 --> 1,2-difluorobutane
- CH3CHFCHFCH3 --> 2,3-difluorobutane
- Above diagram --> trichloromethane
- Above diagram --> 1,2-dichlorobenzene
Alcohol:
- Functional Group:
- -OH
- General Formula:
- R-OH
- Naming:
- Name the parent chain (methane, ethane, propane...)
- Substitute the "-e" ending with "-ol" (propanol, butanol, pentanol...)
- Name other side chains
- Number the locations of the "-OH" on the structure
- Examples:
- C6H5CH2OH --> benzyl alcohol
- CH3 OH --> methanol (methyl alcohol)
- Above diagram --> cyclohexanol
- Above diagram --> ethanol (ethyl alcohol)
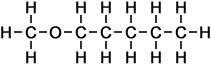
Ether:
- Functional Group:
- -O-
- General Formula:
- R-O-R'
- Naming:
- Visualize the oxygen interrupting the structure, so there are going to be three pieces (in the most basic forms)
- The first part of the structure (for this, we use the side chain prefix: meth-, prop-...)
- The interrupting oxygen (list it as "oxy")
- The last part of the structure (for this, we name it as the parent chain: methane, ethane)
- Combine the first part and the oxygen into one term (methoxy, propoxy)
- And list the final piece as a parent chain (methoxy-methane, propoxy-ethane)
- Examples:
- C3H8O --> methoxy-ethane
- C4H10O--> methoxy-propane
- C5H12O --> methoxy-butane
- Above diagram --> propoxy-pentane
- Above diagram --> methoxy-pentane
Aldehyde:
- Naming:
- Name the parent chain (methane, ethane, propane...)
- Substitute the "-e" ending with "-al" (propanal, butanal, pentanal...)
- Name other side chains
- Number the locations of the "-OH" on the structure
- Examples:
- CH3 CHO --> ethanal
- HCHO --> methanal
- CH3CH2CHO --> propanal
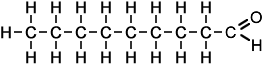
- Above diagram --> nonanal
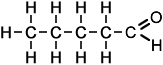
- Above diagram --> pentanal
Ketone:
- Naming:
- Take the prefix of the parent chain (metha-, etha-, propa-...)
- End with the suffix, "-none" (methanone, ethanone, propanone...)
- Name other side chains
- Number the locations of the double-bonded oxygen on the structure
- Examples:
- C7H14O --> 3-heptanone
- C10H20O --> 2-heptanone
- Above diagram --> 2-heptanone
- Above diagram --> 3-nonanone
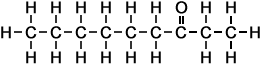
Carboxylic Acid:

- Naming:
- Name the parent chain (methane, ethane, propane...)
- Substitute the "-e" ending with"-oic acid" (methanoic acid, ethanoic acid, propanoic acid...)
- Name other side chains
- Number the locations of the "-OH" on the structure
- Examples:
- CH3CO2H--> acetic acid (ethanoic acid)
- C8H16O2 --> octanoic acid
- C10H20O2 --> decanoic acid
- C4H8O2 --> butanoic acid
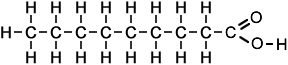
- Above diagram --> nonanoic acid
- Above diagram --> propanoic acid
-Simon Sierra









No comments:
Post a Comment